Table of Contents
ToggleOverview;
Divorce is often envisioned as a taboo topic in many cultures, yet its dynamics can be complex, especially in a diverse nation like India. Despite the global trend towards increasing divorce rates, India maintains relatively low divorce statistics. In this paper, we will explore the reasons behind these low rates, the societal and legal barriers to divorce, and the potential mental health benefits of ending an unhappy marriage.
Divorce in India;
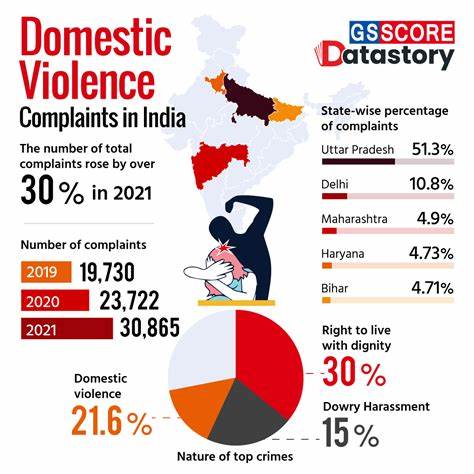
India has one of the lowest divorce rates in the world, with estimates hovering between 1-3%. These figures are remarkably lower compared to Western countries, where divorce rates can exceed 40%. This disparity raises questions about cultural values, legal frameworks, and social stigma surrounding divorce in India.
Cultural Influences;
In India, marriage is traditionally viewed as a lifelong commitment. Factors such as arranged marriages, familial expectations, and societal pressure contribute to the perception that divorce is unacceptable. Many individuals, especially women, may feel compelled to stay in a marriage for the sake of family honour and social approval.
Legal Troubles;
The legal troubles surrounding divorce in India can be multifaceted and often present significant hurdles for those seeking to dissolve their marriages. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Complex Legal Framework; Multiple Personal Laws: In India, marriage and divorce are governed by various personal laws based on religion. This means that different communities (such as Hindus, Muslims, Christians, and others) have their legal frameworks dictating the processes for marriage, divorce, and associated rights. For example:
| Hindu Marriage Act (1955) | Governs marriages and divorces among Hindus. Grounds for divorce include cruelty, desertion, adultery, and irretrievable breakdown of marriage. |
| Muslim Personal Law | Allows for divorce via a process called “Talaq.” However, there have been debates and legal reforms about the practice of instant triple talaq. |
| Christian Marriage Act | Involves a different set of rules and procedures. |
| Special Marriage Act (1954) | This act applies to interfaith marriages or couples who choose civil marriage. The divorce process under this act has its unique legal stipulations. |
2. Lengthy Legal Proceedings: Divorce proceedings in India can be lengthy and complicated, often stretching over several months or even years. Couples might face delays in court schedules, which can prolong the emotional and financial stress associated with divorce.
3. Alimony and Financial Dependency: Deciding on alimony or maintenance can be contentious. The court considers factors such as the duration of the marriage, the financial conditions of both partners and the standard of living during the marriage. There is often a lack of clarity on what is deemed fair, leading to extended negotiations and legal disputes. In many cases, one spouse may have been financially dependent on the other, particularly women. The fear of financial instability can prevent individuals from initiating divorce proceedings, causing them to remain in unhappy or abusive marriages.
4. Child Custody Issues: When children are involved, custody arrangements can be a significant legal complication. Parents may have differing views on custody rights, which can lead to contentious legal battles. Courts determine custody based on the child’s best interest, often delaying the resolution of the divorce process and Disputes over visitation rights can further complicate the situation, requiring additional legal interventions and prolonging emotional distress for all parties involved.
5. Social Pressure: The fear of societal rejection can deter individuals from pursuing divorce despite facing significant problems in their marriages. The legal system can sometimes exacerbate this fear, particularly when lengthy processes and public hearings are involved.
6. Limited Access to Information: Many individuals are unaware of their rights and the divorce process, which can hinder their ability to navigate the legal system effectively. Misinformation about the law can lead to poor decisions and increased legal troubles.
Increasing Divorces;
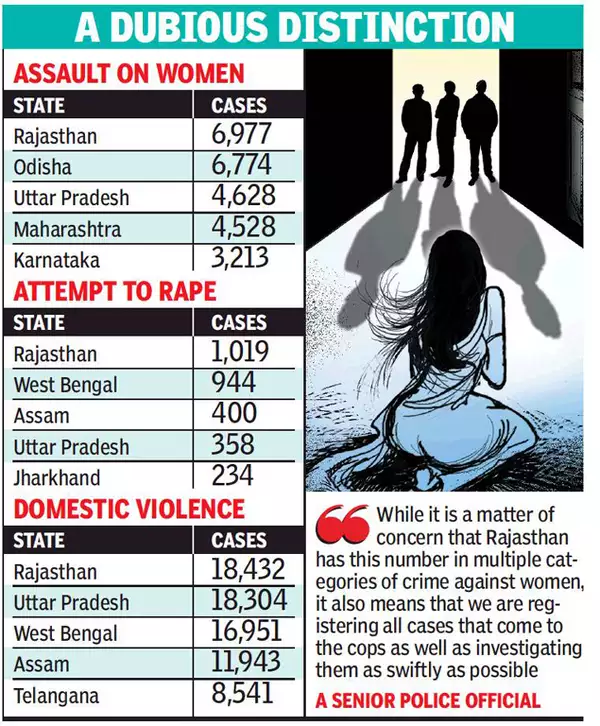
Divorce rates have been increasing in many parts of the world, including India, for a variety of social, economic, and cultural reasons. Here are some key factors contributing to this trend:
1. Changing Social Norms
- Increased Acceptance: Societal attitudes towards divorce have shifted, making it more socially acceptable to end an unhappy marriage. This change encourages individuals to pursue divorce rather than stay in a strained relationship.
- Women’s Empowerment: With the rise of feminism and gender equality movements, women are increasingly asserting their rights, including the right to leave abusive or unsatisfactory marriages.
2. Economic Independence
- Financial Independence of Women: More women are entering the workforce and achieving financial independence. This financial stability enables them to make independent choices regarding their relationships, including the decision to divorce.
- Dual-Income Households: The prevalence of dual-income households can also lead to a reevaluation of marriage dynamics, with partners feeling less reliant on one another and more willing to separate if necessary.
3. Increased Expectations
- Shift in Expectations: Modern relationships often come with heightened expectations regarding emotional fulfilment, companionship, and support. When these expectations are not met, individuals may feel justified in seeking a divorce.
- Love and Happiness: There is a growing belief that marriage should primarily contribute to personal happiness and fulfilment. If individuals feel unhappy, they may view divorce as a solution.
4. Awareness of Legal Rights
- Greater Knowledge of Rights: With improved awareness of legal rights and available support systems, individuals are more likely to seek divorce when facing issues like domestic violence, infidelity, or emotional neglect.
- Access to Legal Resources: Legal frameworks have made it easier for individuals to navigate the divorce process, encouraging more people to pursue separation when necessary.
5. Cultural Shift
- Western Influences: The globalization of culture, including the influence of Western ideals surrounding marriage and individuality, has contributed to changing attitudes toward divorce in many societies.
- Decline of Traditional Arrangements: In many regions, traditional forms of marriage, such as arranged marriages, are on the decline. This shift means that fewer individuals may feel obligated to maintain a marriage that does not fulfil their needs.
6. Pressure and Stress
- Work-Life Balance: The pressures of modern life, including work stress and financial burdens, can strain marriages, leading to increased conflict and potential separation.
- Parenting Challenges: Balancing work and family demands can create tension in relationships, particularly if there are differing parenting styles or expectations.
7. Communication Breakdowns
- Failure to Communicate: Poor communication skills can lead to misunderstandings and unresolved conflicts, contributing to the decision to divorce.
- Lack of Conflict Resolution Skills: Many couples struggle with effectively resolving disagreements, leading to recurring issues that can lead to separation.
8. Mental Health Awareness
- Increased Focus on Mental Health: With growing recognition of mental health issues, individuals are more likely to leave relationships that negatively impact their mental well-being.
Increasing Divorces in Small Towns;
1. Changing Attitudes Towards Marriage
- Evolving Social Norms: Traditional views on marriage and divorce are changing, even in small towns. As societal acceptance of divorce increases, individuals may feel more empowered to leave unhappy relationships without facing significant stigma.
- Increased Awareness: Exposure to different lifestyles and ideologies through media and internet access can lead residents of small towns to reconsider their relationships and the acceptability of divorce.
2. Economic Factors
- Financial Independence: As more individuals, especially women, gain education and job opportunities, they become financially independent. This independence provides them with the means to support themselves outside of a marriage, facilitating the decision to divorce.
- Economic Pressures: Economic challenges, such as job instability and low wages in small towns, can create stress in marriages, leading to conflicts that contribute to divorce.
3. Youthful Marriages
- Early Marriages: In many small towns, people may marry younger due to cultural expectations or lack of opportunities. Young marriages can face more challenges, leading to higher divorce rates among this demographic.
4. Isolation and Limited Support
- Lack of Supportive Services: Although small towns may foster close-knit communities, they often lack the resources available in urban areas, such as counselling and support groups. This can result in unresolved issues within marriages.
- Limited Social Networks: Individuals in small towns might have less access to diverse social networks, leading to limited opportunities for healthy relationship development or for escaping unhealthy situations.
5. Influence of Technology and Social Media
- Awareness and Connectivity: The internet and social media allow people to connect with others outside their immediate community, leading to new perspectives on relationships and potentially inspiring individuals to leave unsatisfying marriages.
- Online Dating and Infidelity: Increased use of online platforms can lead to infidelity or unrealistic expectations about relationships, contributing to marital dissatisfaction.
6. Communication Issues
- Pressure of Expectations: In small towns, traditional roles may still be strong, and individuals may feel pressured to conform to specific expectations in marriage. This pressure can lead to communication breakdowns and dissatisfaction.
- Stigmatization of Counseling: Seeking help for marital issues may be stigmatized in small communities, leading couples to avoid professional help until problems become insurmountable.
7. Impact of Family Dynamics
- Generational Patterns: If divorce is common in a family or community, individuals may be less hesitant to pursue it themselves. Observing the experiences of parents or peers can shape one’s views on the viability of marriage.
- Pressure to Conform: In smaller communities, the pressure to conform to marital norms may lead individuals to marry for the sake of appearances rather than compatibility, resulting in greater disappointment and eventual divorce.
8. Mental Health Awareness
- Increased Recognition of Mental Health Issues: As awareness of mental health grows, individuals in small towns may seek healthier relationships and prioritize their well-being, which can lead to leaving marriages that negatively impact their mental health.
Wider Acceptance of Divorce in Small Towns;
The growing acceptance of divorce in small towns reflects broader cultural shifts, influenced by various social, economic, and technological factors. This shift can be seen as part of a larger societal transformation that acknowledges individual happiness and well-being as paramount. Here are some aspects that contribute to this wider acceptance:
1. Changing Attitudes Toward Marriage
- Less Stigmatization: As communities evolve, the stigma traditionally associated with divorce diminishes. More individuals recognize that ending a marriage is sometimes necessary for personal well-being and happiness.
- Focus on Personal Happiness: There’s an increasing emphasis on individual fulfilment and mental health, leading to a greater willingness to leave unsatisfactory relationships.
2. Cultural Shifts
- Influence of Media and Popular Culture: Television, film, and literature often portray divorce sympathetically, showcasing the complexities of relationships and normalizing separation as a viable option for happiness.
- Celebrity Divorces: Public figures openly discussing their divorces and the lessons learned can influence perceptions, making divorce seem like a more acceptable option.
3. Increased Awareness of Abuse and Toxic Relationships
- Recognition of Abusive Relationships: There is a growing awareness of the harm caused by abusive partnerships, making it easier for individuals to see divorce as a legitimate solution for escaping unhealthy situations.
- Encouraging Empowerment: Social movements advocating for victims of domestic violence and toxic relationships encourage individuals to prioritize their safety and well-being, thus making divorce more acceptable.
4. Support Networks and Resources
- Availability of Counseling and Support Groups: Even in small towns, there is a growing availability of counselling services and support groups, which provide assistance and normalize the conversation around divorce.
- Online Communities: The internet offers access to resources and communities that can support individuals going through divorce, creating a network of understanding and shared experiences.
5. Shifting Social Norms
- Changing Gender Roles: With evolving gender roles, women and men alike are now more likely to prioritize their careers and personal growth. This shift allows for increased agency in making life choices, including divorce.
- Less Pressure to Stay Together: Social norms are gradually shifting away from the idea that couples must stay together at all costs, fostering a more realistic view of the complexities of relationships.
6. Demographic Changes
- Diverse Marital Experiences: As populations in small towns become more diverse, individuals bring different perspectives and experiences regarding marriage and divorce, contributing to broader acceptance.
- Younger Generations: Younger generations, who tend to have different attitudes toward relationships, are more likely to view divorce as a normal and acceptable choice rather than as a failure.
7. Mental Health Advocacy
- Prioritizing Mental Health: Increased focus on mental health has led individuals to recognize that staying in an unhappy marriage can be detrimental to their emotional well-being. This understanding promotes the idea that divorce can be a healthy decision.
- Educational Initiatives: Programs in schools and communities that promote relationship education and mental health awareness help normalize discussions about divorce.
8. Economic Independence
- Financial Empowerment: The rise of dual-income households and women achieving financial independence allows individuals to feel more secure in deciding to divorce without fear of economic instability.
- Job Opportunities: Greater employment opportunities enable individuals to support themselves after a divorce, thereby reducing economic barriers to separation.
Grey/Silver Acceptance of Divorces;
The concept of “grey” or “silver” acceptance refers to an evolving and nuanced understanding of divorce, particularly as it pertains to older adults or long-term marriages. This term signifies a growing recognition that divorce is not only acceptable but can also be a positive choice later in life. Here are some key components associated with this acceptance:
1. Shifting Perspectives on Aging
- Longer Life Expectancy: As people live longer, the motivations for staying in a marriage may change. Older adults are increasingly recognizing the importance of happiness and fulfilment in their later years.
- Redefining Retirement: Retirement is often viewed as a time to pursue individual interests, leading some to reevaluate their relationships and make choices that align with their newfound freedom.
2. Increased Visibility of Late-Life Divorces
- Media Representation: Media portrayals of grey divorces (divorces among older adults) have increased, showcasing individuals who find happiness and fulfilment after ending long marriages.
- Real-Life Stories: Personal testimonies from older adults who have navigated divorce can inspire others, demonstrating that it is possible to have a fulfilling life post-divorce.
3. Empowerment Through Autonomy
- Seeking Fulfillment: Many older adults prioritize their happiness, recognizing that staying in an unfulfilling marriage can diminish their quality of life.
- Personal Growth: Divorce can catalyze personal reinvention, encouraging individuals to explore new interests, relationships, and opportunities.
4. Changing Attitudes Toward Relationships
- Less Traditional Mindset: As societal norms evolve, the notion that individuals must stay in a long-term marriage “at all costs” is gradually fading. Older adults are more likely to embrace the idea that divorce can lead to healthier and happier outcomes.
- Acceptance of Complexity: There is a growing understanding that relationships can be complex; recognizing that love may fade, partnerships may change, or incompatibility may grow over time promotes a more accepting view of divorce.
5. Support Networks and Community Resources
- Increased Resources: Many communities now offer support groups, counselling, and educational resources specifically targeting older adults navigating divorce.
- Social Connections: Communities may foster environments where individuals can connect after divorce, reducing feelings of isolation and encouraging social engagement.
6. Financial Independence and Planning
- Understanding Finances: With increased financial literacy and independence, older adults often feel more secure in making decisions about divorce and its implications.
- Asset Division Awareness: There’s greater awareness of how to manage and divide assets post-divorce, which makes the prospect of leaving a marriage less daunting.
7. Family Dynamics and Acceptance
- Changing Family Structures: Children and extended family members increasingly accept their parents’ decisions regarding divorce, understanding that it can lead to happier family dynamics.
- Encouraging Authentic Relationships: Families may advocate for authentic relationships, supporting loved ones in pursuing a fulfilling life rather than adhering to traditional expectations.
8. Mental Health Considerations
- Focus on Mental Well-being: Older adults are prioritizing mental health, realizing that staying in an unhappy relationship can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Therapeutic Approach: Therapy and counselling services tailored for older adults can facilitate discussions around divorce, helping individuals feel validated in their choices.
The Cost of Divorces;
Positive Impacts
- Incentive for Mediation: High costs encourage couples to consider mediation or collaborative approaches, which can lead to more amicable resolutions.
- Valuing Professional Help: The investment in legal and financial advice can lead to better-informed decisions, potentially resulting in a more equitable settlement.
- Psychological Relief: A quick and decisive resolution, even at a higher cost, can provide emotional closure and allow individuals to move on with their lives.
Negative Impacts
- Financial Strain: High costs can lead to financial hardship for one or both parties, affecting their standard of living.
- Emotional Stress: The financial burden can add to the emotional stress of the divorce process, making it more difficult for individuals to cope.
- Long-term Financial Consequences: Expensive legal fees and ongoing support payments can affect future financial stability and savings.
Awareness Through Bollywood Movies;
“Thappad,” directed by Anubhav Sinha, follows Amrita (Taapsee Pannu), a homemaker whose life unravels after her husband slaps her during an argument. The film delves into the emotional and psychological impacts of this incident, highlighting critical issues like respect, boundaries, and domestic violence in seemingly “normal” marriages.
Key Themes Related to Legal Troubles and Divorce:
- Domestic Violence:
- Legal Framework: The film sheds light on domestic abuse’s emotional and legal repercussions, emphasizing its role as grounds for divorce under Indian law.
- Cultural Stigma: Amrita’s struggle reflects societal pressures that often prevent abused women from seeking legal help or divorce due to fear of ostracism.
- Respect in Relationships:
- The film underscores that respect is fundamental in marriage. Amrita’s decision to seek divorce stems from her realization that violence irreparably damages their relationship.
- Legal and Social Ramifications of Divorce:
- Financial Independence: Amrita’s journey towards divorce highlights the challenges of financial dependency, alimony, and reclaiming personal identity.
- Child Welfare: The film indirectly addresses child custody and welfare issues arising from domestic violence and divorce.
- Societal Change:
- “Thappad” advocates for challenging traditional gender roles and emphasizes women’s rights, encouraging others in similar situations to seek justice and leave abusive relationships.
In summary, “Thappad” is a powerful movie on societal norms, personal relationships, and the legal troubles linked to domestic violence and divorce. It calls for societal change and inspires discussions on respecting and empowering individuals to seek justice and rebuild their lives beyond abusive marriages.
Conclusion:
Divorce remains a challenging and often stigmatized process in India, societal and cultural shifts are gradually transforming perceptions and practices. Recognizing the potential mental health benefits and the importance of personal happiness is crucial to continue advocating for legal reforms and increased awareness to support individuals seeking to end unhappy marriages.


Add a Comment